Canoo Inc.
Summary
- Canoo Inc. is an outcome of ‘business combination’ through Hennessy Capital Acquisition Corp (HCAC), which was established as a ‘blank check company’ for the purposes of merger, acquisition, stock purchase and so on.
- The ‘business combination’ on to take effect on August 17, 2020 and closed it on December 31, 2020.
- The main products of the company include electric van, multi-purpose delivery vehicles, and pickup truck. The company has 805 employees as on December 31, 2021.
- Canoo Inc. went public on December 21, 2020. It is listed and traded on the Nasdaq Global Select Market.
- The company has generated no significant revenue so far from selling of its core products. Net loss before and after taxes of the company during Q’3, 2022 stands at $117,705 thousands, which was $80,875 thousands during the same period a year earlier.
- The company reported net loss of $346,768 thousands for 2021 and $86,686 thousands for 2020. Net loss per share is $1.52 and $0.79 for the years, respectively.
- Cash position of the company has depleted from $702 million to $224 million in 2021.
- Total assets reported is $523 million in 2021, which was $753 million a year earlier.
Brief Company Overview
 Canoo Inc. (NASDAQ:GOEV) is a mobility technology company with a mission to bring electric vehicles (“EVs”) to everyone and provide connected services that improve the vehicle ownership experience. The company is an automotive start-up that develops multipurpose platforms and digital ecosystems to reinvent the automotive landscape in terms of design, pioneering technologies that spans the full lifecycle of the vehicle.
Canoo Inc. (NASDAQ:GOEV) is a mobility technology company with a mission to bring electric vehicles (“EVs”) to everyone and provide connected services that improve the vehicle ownership experience. The company is an automotive start-up that develops multipurpose platforms and digital ecosystems to reinvent the automotive landscape in terms of design, pioneering technologies that spans the full lifecycle of the vehicle.
Birth of the company can be traced back to establishment of Hennessy Capital Acquisition Corp. IV (HCAC) and its incorporation in August 2018 as a Delaware corporation. HCAC was established as a ‘blank check company’ for the purpose of effecting a merger, capital stock exchange, asset acquisition, stock purchase, reorganization or similar business combination with one or more businesses. In the 10-K filing of 2019, the company states its vision to take any opportunity of acquisition in any industry and geographical location but with a preference to match the background of its management; initial target was to acquire one or more businesses with an aggregate enterprise value of $750 million or greater. Later on, the company announced its ‘business combination’ on to take effect on August 17, 2020 and closed it on December 31, 2020.1

The company is headquartered in Torrance California. The main products of the company include electric van, multi-purpose delivery vehicles, and pickup truck. The company has 805 employees as on December 31, 2021. The company is headed by Tony Aquila as an Investor, Executive Chairman, and Chief Executive Officer.
Share Market Insights
Canoo Inc. went public on December 21, 2020. It is listed and traded on the Nasdaq Global Select Market. As on 28 December, 2022 share of the company was trading at $1.60 per share at NasdaqGS. Market capital on the same date is $400.22 million with total number of shares outstanding 345.02 million. Share range of last 52-weeks has been $8.2750 - $1.0200. The company has never paid any dividend and has never done any stock splits up until now. Of the total shares, 18.71% is held by all the insiders, and 31.31% is held by institutions. Top holders of the share of the company include Vanguard Group, Inc, Blackrock Inc., Invesco Ltd., Geode Capital Management, LLC and so on.2
The Business Combination
On December 21, 2020 (the “Closing Date”), Hennessy Capital Acquisition Corp. IV (“HCAC”) consummated the previously announced merger pursuant to that certain Merger Agreement and Plan of Reorganization, dated August 17, 2020 (the “Merger Agreement”), by and among HCAC, HCAC IV First Merger Sub, Ltd., an exempted company incorporated with limited liability in the Cayman Islands and a direct, a wholly owned subsidiary of HCAC (“First Merger Sub”), EV Global Holdco LLC (f/k/a HCAC IV Second Merger Sub, LLC), a Delaware limited liability company and a direct, wholly owned subsidiary of HCAC (“Second Merger Sub”), and Canoo Holdings Ltd., an exempted company incorporated with limited liability in the Cayman Islands (“Legacy Canoo”). Pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement, a business combination between HCAC and Legacy Canoo was effected through the merger of (a) First Merger Sub with and into Legacy Canoo, with Legacy Canoo surviving as a wholly-owned subsidiary of HCAC (Legacy Canoo, in its capacity as the surviving corporation of the merger, the “Surviving Corporation”) and (b) the Surviving Corporation with and into Second Merger Sub, with Second Merger Sub being the surviving entity, which ultimately resulted in Legacy Canoo becoming a wholly-owned direct subsidiary of HCAC (all transactions collectively, the “Business Combination”). On the Closing Date December 31, 2021, and in connection with the closing of the Business Combination, HCAC changed its name to Canoo Inc. and the Company’s common stock (“Common Stock”) began trading on The Nasdaq Global Select Market under the ticker symbol GOEV.
Legacy Canoo was deemed to be the accounting acquirer in the Business Combination based on an analysis of the criteria outlined in Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 805. While HCAC was the legal acquirer in the Business Combination, because Legacy Canoo was deemed the accounting acquirer, for accounting purposes, the transaction was treated as a recapitalization of Legacy Canoo (i.e., a capital transaction involving the issuance of stock by HCAC for the stock of Legacy Canoo). Accordingly, the consolidated assets, liabilities and results of operations of Legacy Canoo became the historical financial statements of the combined company, and HCAC’s assets, liabilities and results of operations were consolidated with Legacy Canoo, upon the consummation of the Business Combination. The net assets of HCAC are recognized at historical cost (which is expected to be consistent with carrying value), with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded.3
Other Contracts
On June 16, 2021, the Company and VDL Nedcar B.V. (“VDL Nedcar”) entered into a binding term sheet for vehicle contract manufacturing (the “Term Sheet”). On July 1, 2021, the Company made a $30.4 million prepayment to VDL Nedcar pursuant to the Term Sheet, which was classified as an investing outflow in the accompanying consolidated statement of cash flows. As of September 30, 2021, VDL Nedcar utilized $4.3 million of the prepayment to purchase property and equipment on behalf of the Company. The remaining $26.1 million was classified as a long-term asset in Other Assets as of September 30, 2021. On December 15, 2021, the Company and VDL Nedcar issued a joint press release announcing that they ceased discussions with respect to the Term Sheet. Upon termination of the Term Sheet, the Company had a right to a refund of the entire $30.4 million prepayment. As such, the $30.4 million prepayment is presented as a receivable in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2021.
On October 19, 2021, the Company entered into an agreement effective October 15, 2021, with Panasonic Industrial Devices Sales Company of America, a Division of Panasonic Corporation of America (“PIDSA”) and Sanyo Electric Co. Ltd., acting through its Mobility Energy Business Division (“SANYO”, and together with PIDSA, “Panasonic”) for the supply of lithium-ion battery cells (the "Panasonic Agreement"). The agreement stipulates an upfront non-refundable $30.0 million payment payable in tranches through March 2022 and provides for cancellable purchases by the Company during an initial purchase period from August 2022 through December 2023. As of December 31, 2021, $15.0 million was paid to Panasonic, $5.0 million due in January 2022 is included in Accounts payable, and the remaining $10.0 million is included in Accrued expenses and other current liabilities. The Company recorded $18.3 million in current assets and $11.7 million in non-current assets.
Financial Analysis
Canoo Inc. is yet to generate any substantial revenue from the sale of its main products. The company finances and plans to finance its operations through commercialization and production with proceeds from the Business Combination, including the proceeds from the PIPE Financing that took place concurrently with the Business Combination, and, as needed, secondary public offerings or debt financings.
Q3’22 Financials
Canoo Inc. has generated no revenue so far. During the period three months up to September, 2022, the company has incurred operating costs of $109,338 thousands compared to $107,006 thousands a year earlier. Added to this expenditure are other expenses like interest expense, loss on fair value change in contingent earnout shares liability, and loss on extinguishment of debt. Thus, net loss before and after taxes of the company stands at $117,705 thousands, which was $80,875 thousands during the same period a year earlier. Net loss per share stands at $0.43 for this period and $0.35 for the period earlier. At the end of third quarter on September 30, 2022, the company reported its current assets at $40,412 thousands and total assets at $444,786 thousands which was reported at $291,306 thousands and $523,074 thousands. The big difference is due to the decrease in cash position from $224,721 thousands to $6,815 thousands.
The company has current convertible debt in its portfolio. It also has contingent earnout shares liability and operating lease liability in its portfolio as long-term liabilities. Total liabilities of the company stood at $216,915 thousands in this period, and it was $179,075 a year earlier. The company has $0.0001 par value 10,000 preferred shares authorized but no shares issued as on September 30, 2022. Canoo Inc. has $0.0001 par value 500,000 common stock authorized; 299,868 and 238,578 issued and outstanding at September 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively.
Cash used in operating activities during the first three quarters of this financial year is $329,863 thousands, which was $180,621 thousands during the previous period. The company purchased new property, plant, and equipment. Therefore, cash used in investing activities during the first nine months of the financial year is $58,377 thousands, which was $100,110 thousands. In absence of revenue and profits, the company has financed all the cashflows used in operating and investing activities. During this first nine months, the company has received proceeds from purchase of shares and warrants by VDL Nedcar, from issuance of shares under SEPA agreement, from issuance of shares under PIPE and from employee stock purchase plan. Thus, proceeds from financing activities this first nine months stand at $181,271 thousands, which was $5,377 thousands.
Analysis of annual financials
Income Statement Analysis
Revenue
The company has generated no revenue in the year 2021. But in 2020, it has reported revenue of $2.6 million generated from the provision of engineering, development and design consulting services on a project basis. Cost of revenue, excluding depreciation expense, was $0.7 million in the year ended December 31, 2020. The cost of revenue, excluding depreciation for year ended December 31, 2020 includes materials, labor, and other direct costs related to the provision of engineering, development, and design consulting services. There is no cost of revenue associated in 2021.
Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses increased by $103.4 million, or 72.4%, to $246.2 million in the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to $142.9 million in the year ended December 31, 2020. The increase was primarily due to increases in research and development costs of $92.5 million and salary and related benefits expense of $38.8 million, partially offset by a decrease in stock-based compensation expense of $33.6 million. The increase in research and development costs primarily is related to expenditures for the Gamma stage engineering design and development costs incurred during the year ended December 31, 2021.
Salary and related benefits expenses increased $38.8 million, from $48.2 million in the year ended December 31, 2020 to $87.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2021. These increases are primarily due to continued investment in personnel and contract employees to drive and reach the company’s research and development goals.
The decrease in stock-based compensation expenses of $33.6 million was primarily driven by the restricted stock awards modified and issued during the year ended December 31, 2020. This decrease was largely due to $58.7 million of stock-based compensation incurred in 2020 related to the modification of the performance restricted stock awards to time-based vested awards with a merger trigger, which was satisfied on December 21, 2020, partially offset by the recognition of stock compensation expense related to issuance of awards to employees during the year ended December 31, 2021.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased by $143.1 million, or 277.3%, to $194.7 million in the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to $51.6 million in the year ended December 31, 2020. The increase was primarily due to increases of $57.7 million in stock-based compensation expenses, $41.3 million in professional fees, $17.2 million in salary and related benefits, $11.2 million in occupancy costs, and $6.1 million in marketing and events. Other factors affecting selling, general and administrative expenses were individually immaterial.
The increase in stock-based compensation expenses of $57.7 million was primarily driven by certain awards granted during the year ended December 31, 2021 subject to time, performance and market vesting conditions, primarily in the form of restricted and performance stock units. The remaining increase was primarily driven by the continued recognition of stock compensation expense, resulting from the modification of certain performance restricted stock awards to become time-based vesting with a merger trigger, which was satisfied on December 21, 2020.
Interest Expense
Interest expense decreased by $10.6 million in the year ended December 31, 2021. The decrease was primarily due to interest expense incurred and the amortization of debt discount on related party convertible notes that were repaid in connection with the Business Combination.
Gain on fair value change in contingent earnout shares liability
As part of the Business Combination, certain stockholders and employees are entitled to receive additional shares of the company’s Common Stock (“Earnout Shares”) to be issued when the Common Stock’s price reaches certain market share price milestones within specified periods following the Business Combination on December 21, 2020. Canoo Inc. recognized a non-cash gain on the fair value change of contingent Earnout Shares liability of $104.4 million and $115.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively, which was a result of the periodic remeasurement of the fair value of contingent Earnout Shares liability.
The company reported net loss of $346,768 thousands for 2021 and $86,686 thousands for 2020. Net loss per share is $1.52 and $0.79 for the years, respectively.
Cash Flow Statements Analysis
Net cash used in operating activities was $300.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2021. Cash outflow from operating activities primarily consists of payments related to research & development and selling, general and administration expenses. Total expenditure as it relates to research & development excluding depreciation was $246.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2021, of which $25.8 million is related to stock-based compensation expenses during the year. The Company also incurred selling, general and administration expenses of $194.7 million for year ended December 31, 2021, of which $82.6 million is related to stock-based compensation expenses during the year. The expenses include salaries and benefits paid to employees as primarily all salaries and benefits are paid in cash during the year.
Net cash used in investing activities was approximately $162.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, which primarily consisted of purchases of fixed assets that are recorded in construction in progress specifically related to the development of manufacturing lines as well as equipment and tooling necessary in the production of the Company’s vehicles. Net cash used in investing activities was also comprised of the prepayment made to VDL Nedcar. Net cash used in investing activities was $7.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, which primarily consisted of purchases of machinery and equipment as well as computer hardware and software.
Net cash used in financing activities was $11.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, which was primarily due to the $11.3 million in payments for offering costs. The $6.9 million repayment of the PPP loan during the year was offset by $6.9 million in cash received from exercise of public warrants. Net cash provided by financing activities was $787.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, which was primarily due to the proceeds of $607.1 million from the Business Combination, net of transaction costs and advisory fees, issuance of convertible notes totaling $180.5 million and proceeds from long-term debt borrowing of $7.0 million, partially offset by merger offering costs of $5.8 million and payment on stock warrant redemption of $0.8 million.
Balance Sheet Analysis
Cash position of the company has depleted from $702 million to $224 million in 2021. Prepaids and other current assets has increased during this year from $6 million a year earlier to $64 million. In that amount exists the advance of $30 million to be returned from VDL Nedcar. Investment of the company in property, plant and equipment has increased significantly from $30 million $202 million. Total assets reported is $523 million in 2021, which was $753 million a year earlier.
Total current liability of the company stands at $136 million in 2021, up from $27 million a year earlier. Among the long-term liabilities, the company has Earnout Shares liability. As of December 21, 2020, the initial fair value of Earnout Shares liability was recognized at $248.9 million with a corresponding reduction from the additional paid-in capital in stockholders’ (deficit) equity. As of December 31, 2021, and 2020, the fair value of the company’s Earnout Shares liability was estimated to be $ 29.1 million and $133.5 million, respectively. The Company recognized a gain on the fair value change in Earnout Shares liability of $104.4 million and $115.4 million as other income in consolidated statement of operations for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. The company has a lease liability of about $13 million both in this year and a year earlier. Total liabilities of the company stand at $179 million in 2021 and $188 million in 2020.
Canoo Inc. reports additional paid in capital of $1,036 million in 2021, which was $910 million a year earlier. After adjusting for accumulated deficit, stockholder’s equity stands at $343 million in 2021 and $565 million in 2020.
Business Overview
Canoo Inc. builds a platform to capture value across the entire vehicle lifecycle and across multiple owners. The company builds platforms and data architecture as a part of its multi-layer business model that will serve as the foundation for the vehicles the company intends to offer. The foundational layer in this model is their Multi-Purpose Platform (“MPP” or “platform”) architecture, which serves as the base of the vehicles, including the Lifestyle Vehicle and its Delivery, Base, Premium, and Adventure trims; the Multi-Purpose Delivery Vehicle (“MPDV”) and the Pickup. The next layer is cybersecurity which is embedded in the vehicle to ensure the privacy and protection of vehicle data. The top hats, or cabins of the company are modular and purpose-built to provide tailored solutions for their customers. The remaining layers are the connected accessories and digital customer ecosystem. With the help of this layer, owners will be able to customize their vehicles by adding connected accessories such as Bluetooth devices or infotainment systems. In addition, there are opportunities for software sales throughout the vehicle life, including predictive maintenance and service software or advanced driver assistance systems (“ADAS”) upgrades.
Products
The products of the company can be classified into four categories – Lifestyle Vehicle, MPDV, Pickup Truck and Platform.
Lifestyle Vehicle
This vehicle is fully electric and suitable for city explorers, businesses, families and adventurers. The company expects to launch this product by the end of 2022 starting approximately at $39,950. It has 200 miles range, up to 350 horse power capacity, and 121 cubic feet cargo volume. The vehicle will be available in three variants – Base, Premium and Adventure. The base variant will have up to 350 horse power capacity, 5 seats. It will charge from 20% to 80% in 28 minutes. Wheel diameter of this variant is 18 inches. The premium variant has 7 seats, panoramic glass roof and street view window. The adventure variant has exclusive dark green colour, light bar and roof rack, and 19 inches adventure wheel.
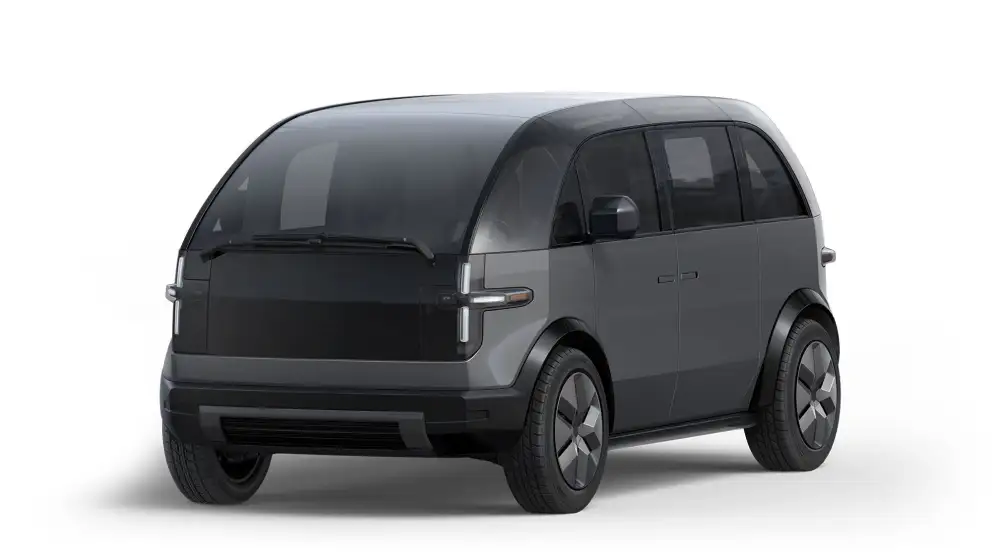

MPDV
MPDV stands for Multi-Purpose Delivery Vehicle. It is a multi-purpose delivery vehicle. The company positions the product on that it would offer lower total cost-of-ownership, easy maintenance, more cargo volume, small footprint, and easy maneuverability. The vehicle will also include some productivity tools such as power plant, and scope to plug in the tools of the owner.
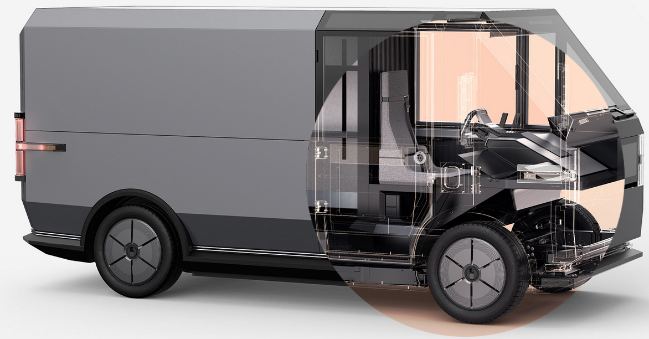
Pickup Truck
This product is designed to function for both work and weekends. Targeted capacity for the truck is 500+ horse power, payload capacity is up to 1800 pounds, range is 200+ miles, and power train is AWD or RWD.4
Platform
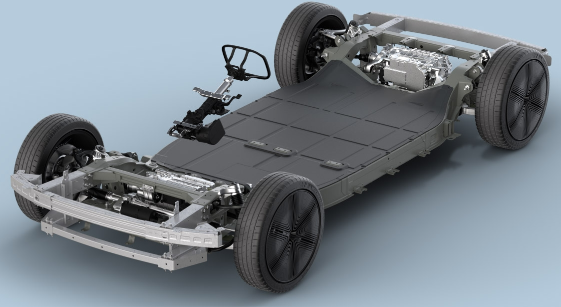
Canoo boasts its ‘unique independently drivable’ platform. The platform will have ‘first true steer-by-wire-platform’. The battery moduled are directly incorporated into the platform structure. Also, it offers in-house designed ECUs and battery management systems (BMS). The platform incorporates composite leaf spring suspension.
Competition and Industry Analysis
Features and competitive edge
Canoo Inc. is trying to innovate new processes, platforms, features, and value-additions in order to keep a competitive edge in the market. The company is doing research to improve the current electric vehicles that are in the market. The company believes its “Multi-purpose Platform” to be the world’s most modular, flattest, production-ready EV platform. The platform is designed to provide maximum cargo space, offer lower cost and maximum value. The platform is to be used for all four lines of products of the company, which will reduce cost and time of research, testing and manufacturing. This proprietary platform of the company has following features which are claimed to the first in the market.5
- True Streer-by-Wire
- Leaf spring suspension system
- Advanced drive train systems
- Battery and battery management systems
- “DC fast charge” and bi-directional charging capabilities
- Innovative electrical systems architecture
“Canoo Digital Escosystem” is being developed by the company which should serve as a major point of differentiation between Canoo and its competitors. The application will give opportunity to the customers to connect all their Canoo vehicles throughout the lifecycle of them, and a raw data opportunity of 1-2 terabytes per day. A core value proposition of the offering is its ability to centralize and analyze data from not only Canoo vehicles, but all other vehicles, across multiple owners. The ecosystem aims to collect data over-the-air from Canoo and other connected vehicles, and via an OBD device from non-connected vehicles. The company will package some functionalities with the vehicle, while others are expected to be offered as upgradeable options which may be purchased or accessed as a subscription service. In addition, Canoo plans to assess partnerships with third-parties for certain services accessed through their software, such as financing or insurance. The Canoo Digital Ecosystem, designed to offer long-term return on capital for customers, will leverage this data to power a vehicle lifecycle management platform, delivering an improved customer journey.6
As a part of the manufacturing strategy, the company has decided to locate its production plants in America to engage with the communities that are investing in high tech, and innovative manufacturing alongside them and to create American jobs as well. It will use manufacturing technologies such as 3D-printing, and flexible machinery and equipment. Currently, Canoo has secured commitments with the states of Arkansas and Oklahoma for manufacturing, R&D, software development and customer support and finance facilities. The company is in the process of completing definitive agreements with both states including approximately $400 million of non-dilutive financial incentives. It intends to have an advanced industrialization facility located in Bentonville, Arkansas, capable of producing vehicles at low volume. By initiating production of vehicles in the advanced industrialization facility in Bentonville, the company will also be able to validate and test their processes in advance of starting scaled production at their high-volume commercial production facility in Pryor, Oklahoma.
Canoo Inc. has revealed the MPDV in December, 2020 and the Canoo Pickup in March, 2021. The research and development team of the company is developing prototypes of Lifestyle Delivery Vehicles which will pave the ways for MPDV, Canoo Pickup and other derivatives of Lifestyle Vehicle. To achieve an overall five-star US New Car Assessment Program (“NCAP”) crash rating, the company has conducted thousands of computer-aided engineering (“CAE”) crash simulations.
The company expects to offer direct sales through their website for fleets, individuals, and volume orders. They are also exploring vehicle sales through alternative distribution channels, including physical retailers and online sales platforms, which may offer access to existing markets and sales channels, reduce capital expenditure, and allow for more rapid and seamless expansion to new markets, both urban and non-urban. The company expects to generate more revenue from the sale of its aftermarket products. Canoo Digital Ecosystem will also be another source of revenue for the company. Subscription models will be handed out to the customers for using premium features. For service and maintenance, the company plans to develop their own service facilities or to operate via third-party partnerships where possible, so that owners of our vehicles can receive fast and seamless service wherever they are.
Market Opportunity
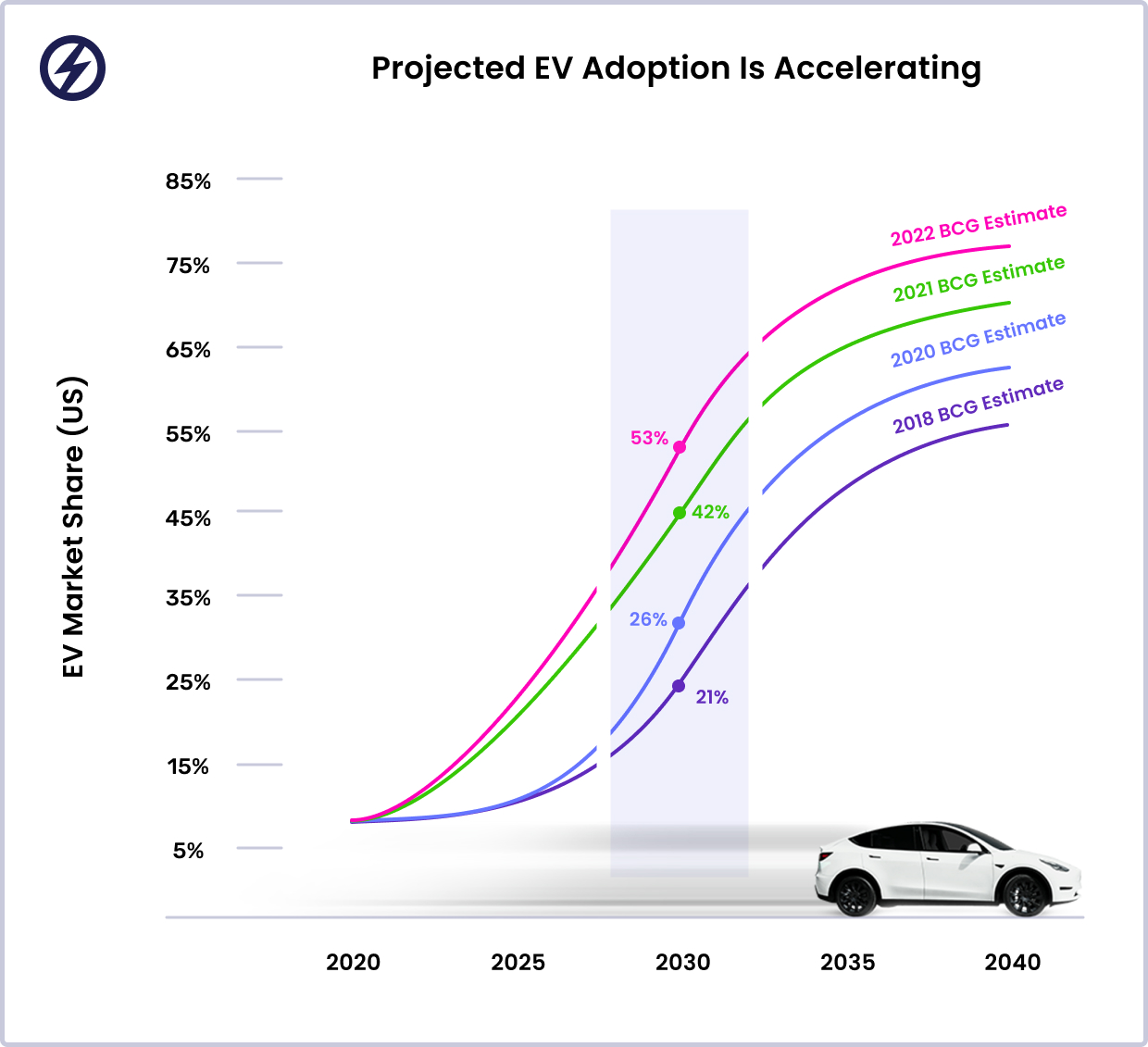
The market for Electric Vehicles can be broadly categorized into two segments – passenger and commercial applications. The global call for clean energy has spurred the governments pass laws to move from gasoline vehicles to electric vehicles market. Since 2018 Boston Consulting Group (BCG) has been publishing reports on projection on the EV adoption. As the years have passed, the company has revised the sales projection of EVs in 2030. In 2018 report of BCG, the projection was 21% and in 2022 report, the project is revised to achieve CAGR of 53% year-on-year. BCG’s 2022 report was published in June of 2022, months before the new tax credits in the Inflation Reduction Act (signed August 2022) and California’s proposed ban on the sale of gasoline vehicles in 2035 (announced August 2022). These developments will continue to expedite EV adoption in the US, promising that the next BCG report will have more aggressive projections.7
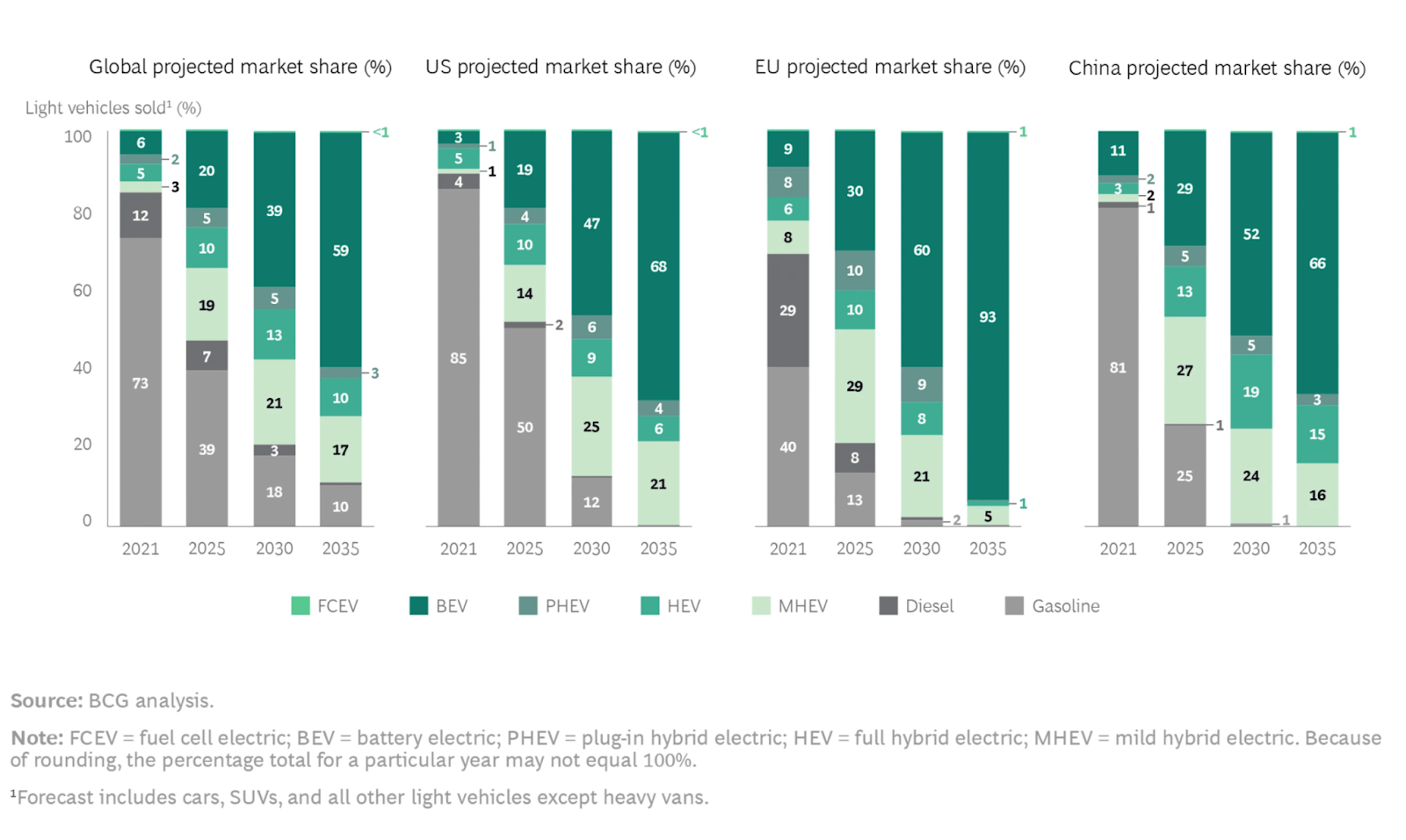
The commercial market segment for Canoo supposedly has huge opportunity in it. The last mile delivery vehicles are expected to be into the market keeping a same pace with the growth of the ecommerce. According to eMarketer, the North American e-commerce market is projected to grow at a 18.4% CAGR (between 2019 and 2025), reaching approximately $1.6 trillion in scale by 2025. Further, the transition of existing and new last mile delivery fleets to all EVs is expected to be a significant trend in the short-term period, according to McKinsey. According to Bloomberg NEF, light duty commercial vehicles, such as last mile delivery vehicles, will be the first commercial vehicles to transition to electric, as compared to medium and heavy-duty commercial vehicles.
According to Bloomberg NEF, global sales of new passenger EVs are expected to grow from 2.7% of total vehicle sales in 2020 to 10% and 58%, in 2025 and 2040, respectively. Consumers, facing the growing threat of climate change and becoming more confident in improved EV range and the broader expansion of EV charging infrastructures, are increasingly looking to an EV as their next vehicle. Consumers in urban areas, in particular, have shown the highest levels of demand. Demand for passenger EVs in the United States, specifically, is expected to grow quickly at a 26% CAGR from 2019 to 2028 and reach over 3 million EVs on the road by 2028, according to EVAdoption. Potential significant upside in the consumer EV segment remains as the penetration of EVs in the United States as a percentage of total annual consumer vehicle sales is expected to still be under 3% in 2022, according to data from Bloomberg NEF, presenting substantial growth potential for our consumer vehicle offerings.
Competitive strengths
- Differentiated digital ecosystem is considered by the company to be a major source of competitive advantage.
- The company will offer aftermarket services throughout the lifetime of the vehicles. Incremental opportunities can arise from their durable MPP, adaptable top hats, customizable connected accessories, automotive service-related software offerings and over-the-air upgrades.
- The in-house engineered and designed platform can give the company a competitive advantage.
- The ecosystem is built as a software-centric one, which can provide harmonized vehicle data services and monetization opportunities.
- The company also reports its experienced leadership with a long track record of success and deep expertise in automotive vehicle lifecycle technologies as its competitive advantage.
Recent Developments
- Canoo Inc. entered into an agreement in November, 2022 to acquire a Vehicle Manufacturing Facility in Oklahoma City. Strategically located with easy access to road and rail, the facility will produce Canoo’s LDV and LV vehicles for delivery to customers in 2023. With a dedicated training center, Canoo’s Vehicle Manufacturing Facility will employ more than 500 people and be equipped to ramp to a 20,000 unit annual run rate by the end of 2023, with additional capacity to scale on the 120+ acre site.8
- On Oct 17, 2022, Kingbee placed binding order for 9,300 Canoo Electric Vehicles and on Oct 11, 2022, Zeeba singed binding agreement to purchase 3,000 Canoo Electric Vehicles. And in July, 2022, Walmart signed to purchase 4,500 Canoo Electric Vehicles to be used for their last mile delivery.
- ^ See 10-K Filing 2019
- ^ All the information is taken from Yahoo Finance
- ^ For further info, see 10-K Filing 2020
- ^ More about this product at https://www.canoo.com/pickup/
- ^ For further details see 10-K filing, 2021
- ^ https://techcrunch.com/2021/06/17/canoo-wants-to-connect-owners-to-all-of-their-vehicles-not-just-canoos/
- ^ https://www.recurrentauto.com/research/ev-adoption-us
- ^ https://www.press.canoo.com/press-release/canoo-to-acquire-vehicle-manufacturing-facility-in-oklahoma-city