Indus Towers Ltd
Summary
- Indus Towers Limited is formed by the merger of Bharti Infratel Limited and Indus Towers
- Indus Towers Limited has over 183,462 towers and 332,551 co-locations and a nationwide presence covering all 22 telecom circles.
- Indus’ leading customers are Bharti Airtel, Vodafone Idea Limited and Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited

Company Overview
Indus Towers Limited (NSE:INDUSTOWER) is formed by the merger of Bharti Infratel Limited and Indus Towers. This combined strength makes Indus one of the largest telecom tower companies in the world.1
Enabling communication for millions of people daily, Indus will continue to provide affordable, high-quality and reliable services for the growing network connectivity needs of India.
Indus Towers Limited has over 183,462 towers and 332,551 co-locations (as on 30th September 2021) and a nationwide presence covering all 22 telecom circles. Indus’ leading customers are Bharti Airtel (together with Bharti Hexacom), Vodafone Idea Limited and Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited, which are the leading wireless telecommunications service providers in India by revenue.
The Company is committed to truly living its credo of Putting India First and Connecting Lives Across the Nation.

Product and Services
The company's product and service portfolios are designed around these three core elements and aim to enhance uptime, coverage and service quality while lowering operational costs for customers and minimizing its carbon footprint.2
Products
Tower - For Mounting the Operator Antennae at an Appropriate Height
The company deploy the passive physical infrastructure necessary to house the active equipment – the base transceiver station, transmission link and microwave antenna – of its customers. Towers range from the traditional lattice type structure – such as the ground-based tower, rooftop tower or pole – to aesthetically designed lightweight hybrid poles, monopoles or camouflaged towers that merge with the backdrop.
Power - For Providing Uninterrupted Energy Supply to Telecom Equipment
The company provide innovative energy solutions for powering its customers’ active equipment in a cost-effective way. Wherever possible, the company power its towers using grid energy from state electricity boards. Diesel is utilised where reliable grid energy is not available.
Space - For Housing Telecom and Power Equipment
The company acquire the requisite space from residential and commercial property owners – its landlords – for placing its passive infrastructure at strategic locations. The company engage with landlords throughout the lifecycle of hosting telecom infrastructure on their premises.
Smart Cities - In pioneering Smart City partnerships with New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC), Vadodara Municipal Corporation (VMC), Dehradun Smart Cities (DSCL) and Bhopal Smart City (BSCDCL), Indus Towers has rolled out its Smart Digital Infrastructure of Smart poles LED lights, CCTV cameras, Variable Digital Messaging Board, Environment Sensors, City Public Wi-Fi including the fiber backbone.

Services
Tower Operations Center (TOC)
The Indus Tower Operations Center (TOC) is a state-of-art facility that is designed to cater to one of the most fundamental requirements for company-wide operations. Customer Delight remains at the centre of everything the company do from the facility. With its service footprint expanding to 22 telecom circles across India, its new TOC is the biggest operations in the NOC industry, managing 200+ Operations Support System under one roof. The NextGen offering provides services across all business functions, including Operations, Energy, Estate, Revenue Assurance, Technology, and Human Resource. It’s a combination of Man and Machine, enabled by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML).
The TOC provides round-the-clock surveillance services to all of Indus’ telecom sites across India through centrally managed operations. The programmed surveillance provides actionable insights on-the-go to the field personnel via an automated calling system followed by an SMS. Real-time alerts on faults enable improved tracking and maintenance to ensure the network infrastructure is always up and running. The company's Cloud-based call center enables prompt servicing across all circles and features real-time monitoring of calls. Moreover, each call being made from the TOC is accompanied with the full History of Site to improve operational efficiency and effectiveness.
Green Technology
Green Sites - The company's towers are powered through either grid-sourced electricity or diesel generators. In 2011, the company became the first company to introduce Green Sites and Green Cities, which are not just diesel-free, but also demonstrate top-range network performance.
Energy Solutions
The company found that majority of energy in telecom tower shelters was being consumed by air conditioners rather than active telecom equipment in order to keep instruments at the ambient temperature. This set in motion its Shut AC initiative that sought to replace air conditioners with free cooling units, which consume less energy and are specifically designed to control the internal environment of cell site enclosures.
The company initiated the Indoor-Outdoor conversion, achieved through natural cooling that works on the principle of flow of air in differential temperatures. The Shut DG: Green Sites project was conceived to run telecom network operations without using diesel as power backup, by instead running the network on a more environment-friendly advanced battery bank solution, without compromising on the network uptime.

Industry Overview
Indian Telecom Industry
The Indian telecom market is the second largest in the world in terms of the number of subscribers with a wireless subscriber base of 1.16 Bn (as of January 31, 2021). Wireless broadband base now stands at 734.26 Mn (as of January 31, 2021) representing a wireless broadband penetration of ~54%. Source: TRAI.3
The Indian telecom market has seen an exponential growth in subscribers and wireless data volumes in last few years driven by affordable tariffs, newer technologies providing faster services, everexpanding network coverage and capacity, ecosystem enhancement from handsets to content along with apps and use cases for data, overall economic development and digitization initiatives across private and public sector, regulatory developments, etc.
According to Nokia MBiT Index Report 2021, post introduction of 4G services in 2014-15, total data traffic increased by ~60 times (2015-2020), one of the highest in the world and average monthly data usage per user has increased almost 17 times in these five years, a CAGR of 76% p.a. Strong trends continued in 2020, with total traffic increasing 36% YoY and average monthly data traffic per user increased by 20.4% YoY, driven by continued upgradation to 4G & increased online traffic due to COVID-19. Increased online education, remote working across sectors and higher Over-the-top (OTT) viewership were among the reasons that have contributed to the data traffic growth.
With the continued migration from 2G/3G to 4G, introduction of 5G, launch of low cost 4G smartphones, the wireless growth trends are expected to continue in the future. Another segment that is expected to come in the limelight is fixed broadband through fixed wireless access (FWA) and FTTx, as digital services such as e-commerce, e-payments, online education and entertainment continue to grow in the country. 5G spectrum auctions likely in 3.3-3.6 GHz band expected in the near future and potentially mm Wave band could further boost FWA as a cost-effective broadband alternative.
Indian Telecom Infrastructure Industry
The Indian Telecom Infrastructure industry boasts of IP-I registration holders that establish and maintain assets such as towers, Right of Way (ROW), duct space and dark fiber for the purpose to grant on lease/rent/sale basis to the Licensees of Telecom Services under Section 4 of the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885.
Over the years, IP-1 players have played an important role in the proliferation of affordable wireless services in the country by creating shared infrastructure for the Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) which ensures opex and capex efficiencies, faster time-to-market and avoids any duplication across the value chain which would otherwise lead to wastage of resources.
India has been at the helm of passive infrastructure sharing, a model that has been emulated globally. Since 2010, number of towers has quadrupled to reach more than 600,000 towers at present providing ubiquitous quality services to 1.16 Bn consumers (Sep’20 – Source: E&Y/ TAIPA).
2021 Spectrum Auction: On January 6, 2021, the DoT invited applications for a total quantity of 2308.80 MHz across frequencies in the 700 MHz, 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz, 2300 MHz and 2500 MHz bands for a period of twenty years. On March 2, 2021, the DoT announced successful completion of the auction, with the value of the spectrum for which there were winning bids at H 77,814.80 crore and informed that bidding took place for spectrum in 800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz and 2300 MHz bands. The total quantity of spectrum for which right to use has been acquired in these bands is 855.60 MHz. The participants did not bid in 700 MHz and 2500 MHz bands. Three bidders – Bharti Airtel Ltd, Vodafone Idea Ltd, and Reliance Jio Infocomm Ltd – participated in the auction. Bidder-wise details of quantity of spectrum acquired and amounts payable are as follows:
| Bidder | Total quantity (MHz) | Total amount (Rs crore) |
| Bharti Airtel Ltd | 355.45 | 18,698.75 |
| Vodafone Idea Ltd | 11.8 | 1,993.40 |
| Reliance Jio Infocomm Ltd | 488.35 | 57,122.65 |
Merger Updates
Merger of erstwhile Indus Towers Limited with and into the Company: On April 25, 2018, Indus Towers Limited (formerly Bharti Infratel Limited) (the Company or Transferee Company) and its Joint Venture Company erstwhile Indus Towers Limited (erstwhile Indus or Transferor Company) and their respective shareholders and creditors entered into a scheme of amalgamation and arrangement (under section 230 to 232 and other applicable provisions of the Companies Act, 2013) (Scheme) to create a panIndia tower company operating across all 22 telecom service areas. Subsequently, the Scheme received requisite regulatory approvals including approval from National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT), Chandigarh vide its order dated May 31, 2019 read with its order dated October 22, 2020.
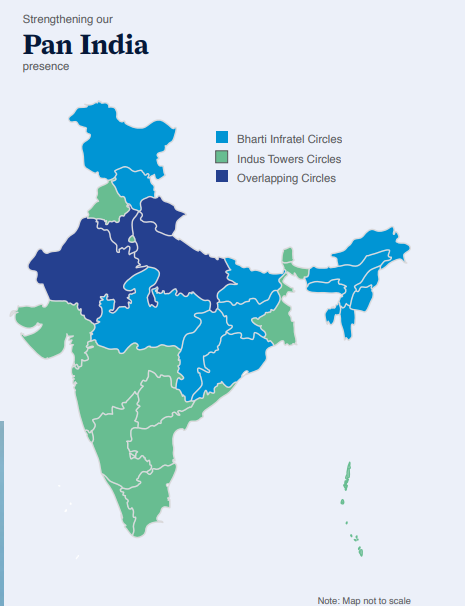
Financial Highlights
Post-merger, the combined strength and highly complementary footprints of both the Companies will enable the company to offer high quality shared passive infrastructure services needed to support the pan-India expansion of wireless broadband services using 4G/4G+/5G technologies for the benefit of Indian consumers and businesses.
As of March 31, 2021, Indus Towers owned and operated 179,225 towers with 322,438 co-locations in 22 telecommunication circles
September 30, 2021 Results
October 25, 2021; Indus Towers announces Consolidated results for the second quarter ended September 30, 20214
Consolidated Revenues for the quarter at Rs. 6,877 Crore, up 8% Y-o-Y
Consolidated EBITDA for the quarter at Rs. 3,641 Crore, up 17% Y-o-Y
Consolidated Profit after Tax for the quarter at Rs. 1,559 Crore, up 38% Y-o-Y
Consolidated Operating Free Cash Flows for the quarter at Rs. 2,109 Crore, up 29% Y-o-Y
Total Tower base of 183,462 with closing sharing factor of 1.81
Indus Towers Limited (Formerly Bharti Infratel Limited) announced its audited Consolidated results for the second quarter ended September 30, 2021. Following the merger between Bharti Infratel Limited and Indus Towers, effective November 19, 2020, the results filed under Regulation 33 and Regulation 52 of the SEBI (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015, as amended, are not comparable with the results disclosed prior to the effective date. Hence, the Company has given proforma unaudited consolidated results. The Consolidated revenue for the quarter was Rs.6,877 Crore, up 8% Y-o-Y. Consolidated EBITDA was at Rs.3,641 Crore, up 17% Y-o-Y and representing an operating margin of 52.9%. The net profit for the quarter was Rs.1,559 Crore, up 38% Y-o-Y. The Operating Free Cash Flow was at Rs. 2,109 Crore up 29% Y-o-Y. The Return on Equity (Pre Tax) increased to 40.9% as against 35.7% on Y-o-Y basis [Return on Equity (Post Tax) increased to 30.9% as against 26.7% Yo-Y basis]. The Return on Capital Employed increased to 23.8% as against 20.6% on Y-o-Y basis.
Bimal Dayal, Managing Director and CEO, Indus Towers Limited (Formerly Bharti Infratel Limited), said:
“This was a significant quarter for the telecom industry in the backdrop of announcement of major reforms which has resulted in sharp improvement in business sentiments. The company welcome this vital step and are prepared to partner with its stakeholders in the journey towards Digital India. The company continued to improve its operational performance with increase in net colocations during the quarter and delivered a strong financial performance.”




