Alcoa Corp
Summary
- Alcoa Corporation is an American multinational corporation that produces and manages primary aluminum, fabricated aluminum, and alumina combined.
- Alcoa Corp is the world's eighth-largest producer of aluminum, with operations in nine countries.
- Alcoa and Emirates Global Aluminium sign new long-term alumina supply agreement

Alcoa Corporation (NYSE: AA, LSE:0HCB) is an American multinational corporation that produces and manages primary aluminum, fabricated aluminum, and alumina combined. It is the world's eighth-largest producer of aluminum, with operations in nine countries.
Recent Developments
Alcoa and Emirates Global Aluminium sign major, long-term alumina supply agreement1
05/15/2023; Alcoa and Emirates Global Aluminium (EGA) announced a new multi-year agreement for Alcoa to supply EGA with smelter grade alumina.
Over the life of the 8-year agreement, which commences in 2024, volume options will allow EGA to procure as much as 15.6 million metric tons of alumina from Western Australia. The supply agreement will represent a significant portion of Alcoa’s annual third-party alumina sales.
The supply agreement will make Alcoa EGA’s largest third-party supplier of alumina. EGA’s Al Taweelah alumina refinery in Abu Dhabi met 47 percent of EGA’s total alumina needs in 2022.
EGA is the largest industrial company in the United Arab Emirates outside of oil and gas, operating smelters in Abu Dhabi and Dubai, an alumina refinery in Abu Dhabi, and a bauxite mine in the Republic of Guinea.
Financial Highlights
First Quarter 2023 Results2
04/19/2023; Alcoa Corporation reported first-quarter 2023 results on April 19, 2023. The company reported adjusted earnings per share (EPS) of $1.03, which beat the consensus estimate of $0.95. Revenues of $3.6 billion were also above the consensus estimate of $3.5 billion.
- Revenue in the first quarter of 2023 was $2.67 billion, down from $2.66 billion in the fourth quarter of 2022 and $3.29 billion in the first quarter of 2022.
- Net loss attributable to Alcoa Corporation was $(231) million in the first quarter of 2023, compared to $(395) million in the fourth quarter of 2022 and $469 million in the first quarter of 2022.
- Earnings per share attributable to Alcoa Corporation were $(1.30) in the first quarter of 2023, compared to $(2.24) in the fourth quarter of 2022 and $2.49 in the first quarter of 2022.
- Adjusted net loss was $(41) million in the first quarter of 2023, compared to $(144) million in the fourth quarter of 2022 and $577 million in the first quarter of 2022.
- Adjusted earnings per share were $(0.23) in the first quarter of 2023, compared to $(0.82) in the fourth quarter of 2022 and $3.06 in the first quarter of 2022.
- Adjusted EBITDA excluding special items was $240 million in the first quarter of 2023, compared to $29 million in the fourth quarter of 2022 and $1,072 million in the first quarter of 2022.

Company Overview
Alcoa is an integrated, upstream aluminum company, mining bauxite, refining alumina, and smelting and casting aluminum. The Company has direct and indirect ownership of 27 locations across nine countries on six continents.3
Joint venture
Alcoa World Alumina and Chemicals (AWAC)
AWAC is an unincorporated global joint venture between Alcoa Corporation and Alumina Limited, a company incorporated under the laws of the Commonwealth of Australia and listed on the Australian Securities Exchange. AWAC consists of a number of affiliated entities that own, operate, or have an interest in bauxite mines and alumina refineries, as well as an aluminum smelter, in seven countries. Alcoa Corporation owns 60% and Alumina Limited owns 40% of these entities, directly or indirectly, with such entities being consolidated by Alcoa Corporation for financial reporting purposes. The scope of AWAC generally includes the mining of bauxite and other aluminous ores; the refining, production, and sale of smelter grade and non-metallurgical alumina; and the production of certain primary aluminum products.
Saudi Arabia Joint Venture
In December 2009, Alcoa entered into a joint venture with the Saudi Arabian Mining Company (Ma’aden), which was formed by the government of Saudi Arabia to develop its mineral resources and create a fully integrated aluminum complex in Saudi Arabia. Ma’aden is listed on the Saudi Stock Exchange (Tadawul). The joint venture complex includes a bauxite mine with estimated capacity of 5 million dry metric tons per year; an alumina refinery with a capacity of 1.8 million metric tons per year (mtpy); and an aluminum smelter with a capacity of 780,000 mtpy.
ELYSIS
ELYSIS Limited Partnership is a joint venture between wholly-owned subsidiaries of Alcoa (48.235%) and Rio Tinto Alcan Inc. (Rio Tinto) (48.235%), respectively, and Investissement Québec (3.53%), a company wholly-owned by the Government of Québec, Canada. The purpose of the ELYSIS joint venture is to advance larger scale development and commercialization of its patentprotected technology that produces oxygen and eliminates all direct greenhouse gas emissions from the traditional aluminum smelting process. Alcoa invented the inert anode technology for the aluminum smelting process that serves as the basis for the ELYSIS joint venture. Batches of aluminum produced by ELYSIS have been sold for use by such companies as Apple Inc. and Audi AG, as the joint venture continues working toward an industrial scale with a technology package planned for sale beginning in 2024.
Others
The Aluminerie de Bécancour Inc. (ABI) smelter is a joint venture between Alcoa and Rio Tinto located in Bécancour, Québec. Alcoa owns 74.95% of the joint venture through the equity investment in Pechiney Reynolds Quebec, Inc., which owns a 50.1% share of the smelter, and two wholly-owned Canadian subsidiaries, which own 49.9% of the smelter. Rio Tinto owns the remaining 25.05% interest in the joint venture.
CBG is a joint venture between Boké Investment Company (51%) and the Government of Guinea (49%) for the operation of a bauxite mine in the Boké region of Guinea. Boké Investment Company is owned 100% by Halco (Mining) Inc.; AWA LLC holds a 45% interest in Halco. AWA LLC is part of the AWAC group of companies and is ultimately owned 60% by Alcoa and 40% by Alumina Limited.
Locations
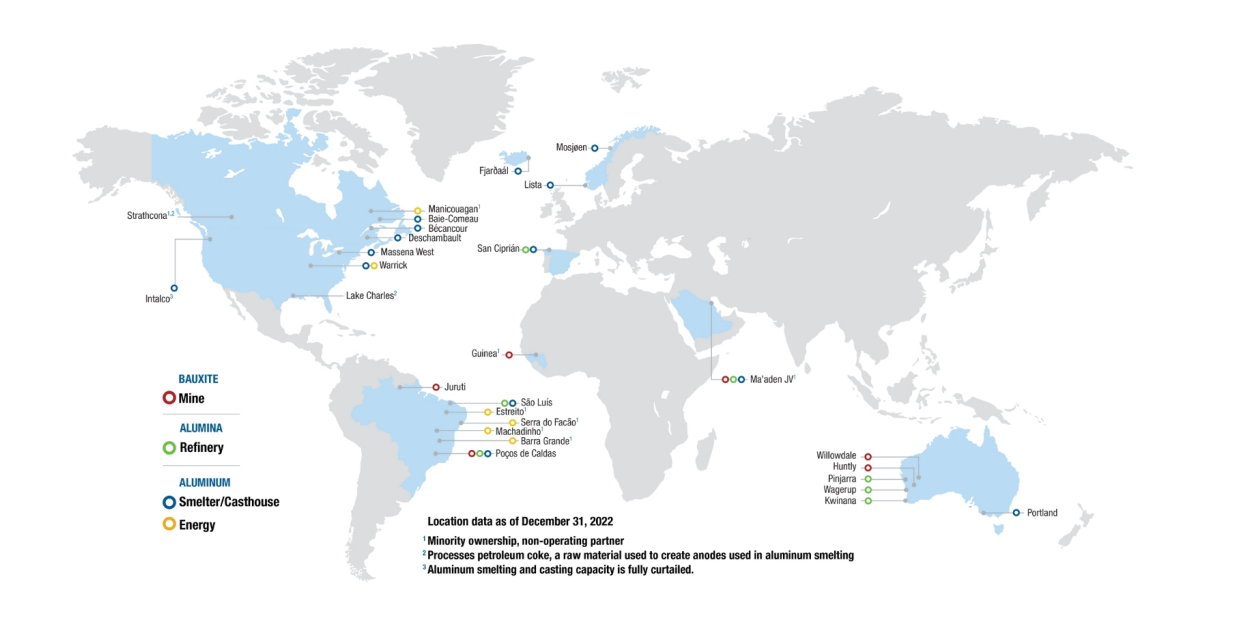
Business Segments
The Company has three reportable business segments: Bauxite, Alumina, and Aluminum.
Bauxite
This segment consists of the Company’s global bauxite mining operations. Bauxite is the principal raw material used to produce alumina and contains various aluminum hydroxide minerals, the most important of which are gibbsite and boehmite. Bauxite is refined using the Bayer process, the principal industrial chemical process for refining bauxite to produce alumina, a compound of aluminum and oxygen that is the raw material used by smelters to produce aluminum metal. The Company obtains bauxite from its own resources, including those belonging to AWAC, as well as through long-term and short-term contracts and mining leases. Tons of bauxite are reported on a zero-moisture basis in millions of dry metric tons (mdmt) unless otherwise stated.
In 2022, Alcoa-operated mines supplied 92 percent of their volume to Alcoa refineries and sold the remaining 8 percent to third-party customers. Alcoa-operated mines produced 36.7 mdmt of bauxite and mines operated by partnerships in which Alcoa, including AWAC, has equity interests produced 5.4 mdmt of bauxite on a proportional equity basis, for a total Company bauxite production of 42.1 mdmt.
On April 30, 2022, Alcoa completed the sale of its investment in MRN. The Company entered into several bauxite offtake agreements with South32 to provide bauxite supply for existing long-term supply contracts.
Alumina
This segment consists of the Company’s worldwide refining system, which processes bauxite into alumina. Alcoa’s alumina sales are made to customers globally and are typically priced by reference to published spot market prices. The Company produces smelter grade alumina and non-metallurgical grade alumina. The Company’s largest customer for smelter grade alumina is its own aluminum smelters, which in 2022 accounted for approximately 30% of its total alumina shipments. A small portion of the alumina (nonmetallurgical grade) is sold to third-party customers who process it into industrial chemical products. This segment also includes AWAC’s 25.1% share of MBAC.
As of December 31, 2022, Alcoa had approximately 1,014,000 mtpy of idle capacity relative to total Alcoa consolidated capacity of 13,843,000 mtpy. Idle capacity of 800,000 mtpy at the San Ciprián refinery is due to the partial curtailment of the refinery in 2022 and 214,000 mtpy of idle capacity at the Poços de Caldas facility is a result of the previous full curtailment of the Poços de Caldas smelter.
Aluminum
This segment currently consists of ![]() the Company’s worldwide smelting and casthouse system and (ii) a portfolio of energy assets in Brazil, Canada, and the United States. The smelting operations produce molten primary aluminum, which is then formed by the casting operations into either common alloy ingot (e.g., t-bar, sow, standard ingot) or into value add ingot products (e.g., foundry, billet, rod, and slab). The energy assets supply power to external customers in Brazil and the United States, as well as internal customers in the Aluminum segment (Baie-Comeau (Canada) smelter and Warrick (Indiana) smelter) and, to a lesser extent, the Alumina segment (Brazilian refineries). This segment also includes Alcoa’s 25.1% share of MAC, the smelting joint venture company in Saudi Arabia.
the Company’s worldwide smelting and casthouse system and (ii) a portfolio of energy assets in Brazil, Canada, and the United States. The smelting operations produce molten primary aluminum, which is then formed by the casting operations into either common alloy ingot (e.g., t-bar, sow, standard ingot) or into value add ingot products (e.g., foundry, billet, rod, and slab). The energy assets supply power to external customers in Brazil and the United States, as well as internal customers in the Aluminum segment (Baie-Comeau (Canada) smelter and Warrick (Indiana) smelter) and, to a lesser extent, the Alumina segment (Brazilian refineries). This segment also includes Alcoa’s 25.1% share of MAC, the smelting joint venture company in Saudi Arabia.

Company History
Alcoa was founded in 1888 by Charles Martin Hall and Alfred E. Hunt.4
- 1886: Charles Martin Hall discovers the process for electrochemically extracting aluminum from bauxite ore.
- 1888: Hall and Alfred E. Hunt found The Pittsburgh Reduction Company, which would later become Alcoa.
- 1893: Alcoa begins commercial production of aluminum.
- 1903: Alcoa builds its first aluminum smelter in New Kensington, Pennsylvania.
- 1910: Alcoa opens the town of Alcoa, Tennessee, to house its employees.
- 1914: Alcoa builds the world's first aluminum aircraft.
- 1920: Alcoa becomes a monopoly in the aluminum industry.
- 1945: Alcoa is forced to break up its monopoly as a result of antitrust laws.
- 1950: Alcoa introduces the Alcoa One-Piece Can, which revolutionizes the beverage industry.
- 1981: Alcoa merges with Reynolds Metals Company to form Alcoa/Reynolds.
- 1986: Alcoa/Reynolds splits into two companies, Alcoa and Reynolds.
- 1999: Alcoa merges with its largest competitor, Alcan.
- 2013: Alcoa spins off its packaging business, forming Novelis.
- 2016: Alcoa sells its alumina business, forming Alumina Corporation of America.
- 2018: Alcoa announces a new $3 billion investment in its aluminum smelting operations.
- 2021: Alcoa reports record revenue of $12.6 billion.
References
- ^ https://news.alcoa.com/press-releases/press-release-details/2023/Alcoa-and-Emirates-Global-Aluminium-sign-major-long-term-alumina-supply-agreement/default.aspx
- ^ https://news.alcoa.com/press-releases/press-release-details/2023/Alcoa-Corporation-Reports-First-Quarter-2023-Results/default.aspx
- ^ https://fintel.io/doc/sec-alcoa-corp-1675149-10k-2023-february-23-19412-2603
- ^ https://www.alcoa.com/global/en/who-we-are/history




