Mastercard Incorporated
Summary
- Mastercard Incorporated is a global technology company in the financial services industry.
- It provides a broad range of payment solutions for consumers, financial institutions, merchants, governments, and businesses.
- Mastercard brands includes Mastercard®, Maestro® and Cirrus®.
- Mastercard present in more than 210 countries and territories.

Mastercard Incorporated (NYSE: MA, LSE: 0R2Z) is a global technology company in the financial services industry. It provides a broad range of payment solutions for consumers, financial institutions, merchants, governments, and businesses. Mastercard's core business is processing payments between the banks of merchants and the card-issuing banks or credit unions of the purchasers who use the Mastercard-brand debit, credit, and prepaid cards to make purchases.
Recent Developments
Mastercard SpendingPulse: U.S. Retail Sales Expected to Grow 3.7% This Holiday Season1
September 19, 2023; This holiday season, running November 1 through December 24, U.S. retail sales excluding automotive are expected to increase 3.7% year-over-year (YOY), according to Mastercard SpendingPulse™. The anticipated growth in retail in the U.S. reinforces continued consumer resilience. Mastercard SpendingPulse measures in-store and online retail sales across all forms of payment and is not adjusted for inflation.
Looking back at the 2022 holiday shopping season, inflationary pricing and pent-up demand, coupled with excess savings and rising wages allowed consumers and retailers to navigate the season well. After years of inventory and spending habits being in flux, the 2023 season will bring a broader rebalancing across categories, channels, and sectors in alignment with macroeconomic trends.
Mastercard SpendingPulse reports on national retail sales across all payment types in select markets around the world. The findings are based on aggregate sales activity in the Mastercard payments network, coupled with survey-based estimates for certain other payment forms, such as cash and check.
Mastercard Introduces a Fast, Safe and Cost-Effective Solution for Businesses to Accept Virtual Card Payments2
July 24, 2023; Today, Mastercard announces the launch of Mastercard Receivables Manager, a new, automated solution that streamlines the way businesses accept and process virtual card payments. The innovation complements Mastercard’s virtual card platform as the company provides choice in payments to players across the ecosystem and accelerates the digitization of B2B transactions across buyers and suppliers.
In an increasingly digital-first world, more businesses are looking to replace cumbersome paper-based payment processes. Virtual cards are rapidly gaining momentum in B2B payments, with over 90% of suppliers reporting that they prefer receiving a digital payment – and the related invoice information - over checks. However, this shift towards emerging tech has also left accounts receivable teams struggling to keep pace with increased virtual card payment processing, underscoring the critical need for an automated solution.
Mastercard Receivables Manager was developed to make virtual card transactions more efficient, secure and cost-effective to process. Suppliers will no longer need to manually capture and enter virtual card details to reconcile the vast number of digital payments received. Instead, the new product consolidates these card payments from all issuers so the remittance data can automatically be matched to open invoices, and formatted and delivered for their Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems - making it easier for suppliers to reconcile invoices with efficiency and accuracy. This also gives suppliers new advantages, including the ability to drive early payments and improve overall visibility of their cash flow.

Financial Highlights
Second Quarter 2023 Results
July 27, 2023; Mastercard Incorporated announced financial results for the second quarter 2023.3
- Second quarter net income of $2.8 billion, and diluted earnings per share (EPS) of $3.00
- Second quarter adjusted net income of $2.7 billion, and adjusted diluted EPS of $2.89
- Second quarter net revenue of $6.3 billion, an increase of 14%, or 15% on a currency-neutral basis
- Second quarter gross dollar volume up 12% and purchase volume up 14%, on a local currency basis
- Net revenue increased 14%, or 15% on a currency-neutral basis. Excluding the impact of Second Quarter Special Items, adjusted net revenue also increased 14%, or 15% on a currency-neutral basis. The increase was attributable to its payment network and its value-added services and solutions.
- Total operating expenses increased 5%. Excluding the impact of Second Quarter Special Items, adjusted operating expenses increased 12%, or 13% on a currency-neutral basis. The increase was primarily due to higher personnel costs.
- Other income (expense) was favorable $268 million versus the year ago period, primarily due to net gains in the current year versus the net losses in the prior year related to unrealized fair market value adjustments on marketable securities. Adjusted other income (expense) was favorable $29 million versus the prior year, primarily due to an increase in its investment income, partially offset by increased interest expense related to its 2022 and 2023 debt issuances.

Company Overview
Mastercard Incorporated is a global technology company in the financial services industry. It provides a broad range of payment solutions for consumers, financial institutions, merchants, governments, and businesses. Mastercard's core business is processing payments between the banks of merchants and the card-issuing banks or credit unions of the purchasers who use the Mastercard-brand debit, credit, and prepaid cards to make purchases.4
Mastercard provides a wide range of payment solutions and services using its family of well-known and trusted brands, including Mastercard®, Maestro® and Cirrus®.
Business Overview
Payment Network
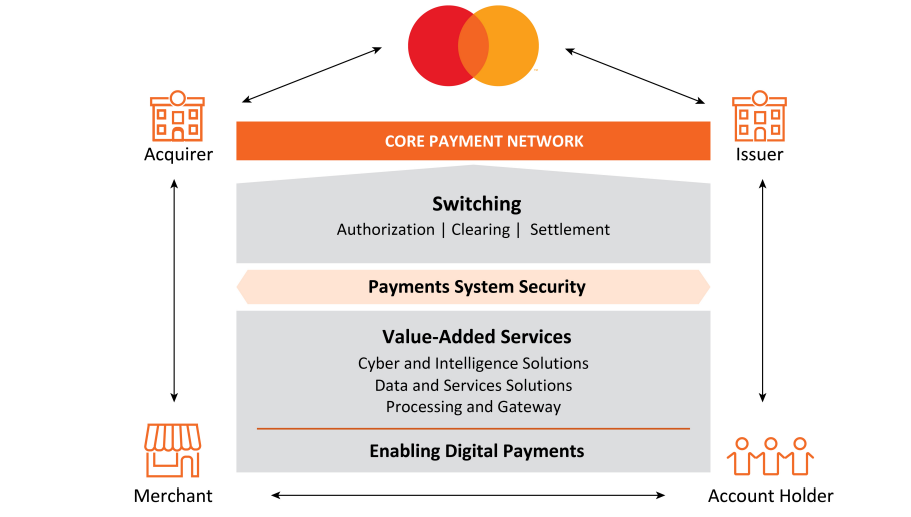
The company's core payment network links issuers and acquirers around the globe to facilitate the switching of transactions, permitting account holders to use a Mastercard product at tens of millions of acceptance locations worldwide.
Payment Network Transactions.
The company's core payment network supports what is often referred to as a “four-party” payments network and includes the following participants: account holder (a person or entity who holds a card or uses another device enabled for payment), issuer (the account holder’s financial institution), merchant and acquirer (the merchant’s financial institution).
The company do not issue cards, extend credit, determine or receive revenue from interest rates or other fees charged to account holders by issuers, or establish the rates charged by acquirers in connection with merchants’ acceptance of its products. In most cases, account holder relationships belong to, and are managed by, its customers.
In a typical transaction, an account holder purchases goods or services from a merchant using one of its payment products. After the transaction is authorized by the issuer, the issuer pays the acquirer an amount equal to the value of the transaction, minus the interchange fee (described below) and other applicable fees, and then posts the transaction to the account holder’s account.
Payment Products and Applications
Consumer Payment Products
Consumer Credit. The company offer a number of products that enable issuers to provide consumers with credit, allowing them to defer payment.
Consumer Debit. The company support a range of payment products and solutions that allow its customers to provide consumers with convenient access to funds in deposit and other accounts. The company's debit and deposit access programs can be used to make purchases and to obtain cash in bank branches, at ATMs and, in some cases, at the point of sale. The company's branded debit programs consist of Mastercard (including standard, premium and affluent offerings), Maestro (the only PIN-based solution that operates globally) and Cirrus (primary global cash access solution).
Prepaid. Prepaid accounts are a type of electronic payment that enables consumers to pay in advance whether or not they previously had a bank account or a credit history. These accounts can be tailored to meet specific program, customer or consumer needs, such as paying bills, sending person-to-person payments or withdrawing cash from an ATM.
New Payment Flows
Disbursements and Remittances. The company offer applications that enable consumers, businesses, governments and merchants to send and receive money domestically and across borders with greater speed and ease.
Commercial Point of Sale. The company offer commercial credit, debit and prepaid payment products and solutions that meet the payment needs of large corporations, midsize companies, small businesses and government entities. The company's solutions streamline procurement and payment processes, manage information and expenses (such as travel and entertainment) and reduce administrative costs.
B2B Accounts Payable. The company offer solutions that enable businesses or governments to make payments to businesses with whom they have a trusted relationship for goods and services.
Consumer Bill Payments. The company offer bill pay solutions to enable consumers and small businesses to pay their billers in a seamless and secure way.

Company History
Seventeen bankers meet in Buffalo, New York to form a federation for the reciprocal acceptance of their credit cards. Interbankard adopts the “i” symbol as its mark. The federation becomes formally chartered in 1967—The Interbank Card Association (ICA).5
- 1967 - Mastercard had its origins in the late 1940s when several U.S. banks gave their customers specially-issued paper that could be used like cash in local stores. In 1966, one of these groups formed the Interbank Card Association (ICA), which later became MasterCard International.
- 1970s - In 1968, ICA began what is now a global network by forming an association with Banco Nacional in Mexico. Later that year, they formed an alliance in Europe with Eurocard. By the late 1970s, ICA had members from as far as Africa and Australia, among other places. To reflect its commitment to international growth, ICA changed its name to MasterCard International. In the 1980s, there was further expansion into Asia and Latin America. In 1987, MasterCard became the first payment card to be issued in the People’s Republic of China. In 1988, the first MasterCard card was issued in the Soviet Union.
- 1985 - In 1985, the company acquired the Cirrus ATM network and the company launched Maestro, the world’s first online point-of-sale debit network, in 1991.
- 2002 - From 2009 to 2012, MasterCard made a series of acquisitions designed to help sharpen its focus on innovation. Among these are Orbiscom, which became MasterCard Labs in 2010 and serves as its incubator for new ideas; DataCash; the prepaid program management business of Travelex (now called Access Prepaid); Trevica; and Truaxis. In 2013, the company acquired Provus, a processor in Turkey.
- 2019 - In January 2019, the company dropped the "mastercard" name from its iconic Brand Mark for many uses. The interlocking red and yellow circles, known as the Mastercard Symbol, can now stand on its own.
References
- ^ https://www.exeloncorp.com/company/about-exelon
- ^ https://investor.mastercard.com/investor-news/investor-news-details/2023/Mastercard-Introduces-a-Fast-Safe-and-Cost-Effective-Solution-for-Businesses-to-Accept-Virtual-Card-Payments/default.aspx
- ^ https://s25.q4cdn.com/479285134/files/doc_financials/2023/q2/2Q23-Mastercard-Earnings-Release.pdf
- ^ https://fintel.io/doc/sec-mastercard-inc-1141391-10k-2023-february-14-19402-629
- ^ https://www.mastercard.com/brandcenter/en/brand-history




