Union Pacific Corporation
Summary
- Union Pacific Corporation operates through Union Pacific Railroad.
- Union Pacific Corporation provides freight rail transportation services throughout the western two-thirds of the United States.
- The Union Pacific Railroad is one of the largest railroads in the United States. It operates over 32,000 miles of track, and it serves more than 230 cities and towns.

Union Pacific Corporation (NYSE: UNP, LSE: 0R2E) operates through Union Pacific Railroad. The company provides a critical link in the global supply chain by linking 23 states in the western two-thirds of the country by rail. The company serve many of the fastest-growing U.S. population centers, operate from all major West Coast and Gulf Coast ports to eastern gateways. The company connect with Canada's rail systems and are the only railroad serving all six major Mexico gateways.
Recent Developments
Union Pacific To Expedite Delivery of Consumer Goods from Port Houston to Five Inland Markets in U.S.1
MAY 30, 2023; Starting June 1, 2023, international shippers will be able to deliver TVs, cell phones and other consumer goods quicker and more efficiently to consumers, as Union Pacific Railroad expands its services at Port Houston to allow intermodal containers to be loaded directly onto railcars and transported by rail to five key metropolitan markets in the United States.
Union Pacific’s new service at Barbours Cut Container Terminal at Port Houston will provide customers direct rail access to five of the nation’s fastest growing metropolitan intermodal markets in Denver, Salt Lake City, Oakland, Los Angeles, and El Paso, reducing truck traffic on its nation’s highways and greenhouse gas emissions.
It also will eliminate the need for containers to be trucked approximately 30 miles from the port to the nearest rail facility in Houston for loading onto rail cars, reducing highway congestion in the Houston area.
CN, UP, and GMXT Announce New Transformational Mexico-US-Canada Intermodal Service
APRIL 24, 2023; CN (TSX: CNR) (NYSE: CNI), Union Pacific Railroad (NYSE: UNP) and GMXT (BMV: GMXT) proudly announced today the creation of Falcon Premium intermodal service, a best-in-class Mexico-US-Canada service with a seamless rail connection in Chicago, Illinois. It will directly connect all CN origin points within Canada and Detroit, Michigan to GMXT terminals in Mexico: Monterrey, Nuevo Leon, and Silao, Guanajuato. This service will directly benefit intermodal customers shipping automotive parts, food, FAK (freight all kinds), home appliances, and temperature-controlled products.
Falcon Premium service will be the fastest, most reliable intermodal rail service between Canada and Mexico by combining the unique benefits of each partner. The seamless service will leverage GMXT’s best-in-class transit times between Silao, Guanajuato, and Eagle Pass, Texas; Union Pacific’s superior route from Texas to Chicago and CN’s best-in-class service connecting Chicago to all points in Canada through the unique EJ&E Chicago bypass.

Financial Highlights
First Quarter 2023 Results2
APRIL 20, 2023; Union Pacific Corporation reported 2023 first quarter net income of $1.6 billion, or $2.67 per diluted share. These results include $107 million in other income from a one-time real estate transaction. This compares to 2022 first quarter net income of $1.6 billion, or $2.57 per diluted share.
- Operating revenue of $6.1 billion was up 3% driven by higher fuel surcharge revenue and core pricing gains, partially offset by a negative business mix and volume declines.
- Business volumes, as measured by total revenue carloads, were down 1%.
- Union Pacific’s 62.1% operating ratio deteriorated 270 basis points. Falling fuel prices in the quarter positively impacted the operating ratio by 190 basis points.
- Operating income of $2.3 billion declined 3%.
- The company repurchased 2.9 million shares in first quarter 2023 at an aggregate cost of $0.6 billion.
- Quarterly freight car velocity was 196 daily miles per car, a 1% decline.
- Quarterly locomotive productivity was 123 gross ton-miles (GTMs) per horsepower day, a 5% decline.
- Average maximum train length of 9,159 feet was flat.
- Quarterly workforce productivity decreased 6% to 991 car miles per employee.
- Fuel consumption rate of 1.123, measured in gallons of fuel per thousand GTMs, deteriorated 1%.
- Union Pacific’s reportable derailment rate improved 10% to 2.21 per million train miles compared to 2.46 for 2022.
Full Year 2022 Results3
JANUARY 24, 2023; Reported net income for full year 2022 was $7.0 billion, or $11.21 per diluted share. These full year results compare to full year 2021 net income of $6.5 billion, or $9.95 per diluted share.
- Operating revenue of $24.9 billion was up 14% driven by higher fuel surcharge revenue, core pricing gains, and volume growth.
- Business volumes, as measured by total revenue carloads, grew 2%.
- Union Pacific’s 60.1% reported operating ratio deteriorated 290 basis points. Higher fuel prices negatively impacted the operating ratio by 20 basis points and the prior period adjustment related to new labor agreements added 30 basis points to operating ratio.
- Operating Income of $9.9 billion was up 6%.
- Union Pacific’s 2022 capital program totaled $3.4 billion.
- The company repurchased 27.1 million shares in 2022 at an aggregate cost of $6.3 billion.
- Union Pacific’s reportable personal injury rate improved 18% to 0.80 per 200,000 employee-hours compared to 0.98 for full year 2021.
- Freight car velocity was 191 daily miles per car, a 6% decline.
- Locomotive productivity was 125 GTMs per horsepower day, a 6% decline.
- Average maximum train length of 9,329 feet was flat.
- Workforce productivity of 1,036 car miles per employee was flat.
- Fuel consumption rate of 1.078, measured in gallons of fuel per thousand GTMs, improved 1%.

Company Overview
Union Pacific Railroad Company is the principal operating company of Union Pacific Corporation. One of America's most recognized companies, Union Pacific Railroad Company connects 23 states in the western two-thirds of the country by rail, providing a critical link in the global supply chain. The Railroad’s diversified business mix includes Bulk, Industrial, and Premium. Union Pacific serves many of the fastest-growing U.S. population centers, operates from all major West Coast and Gulf Coast ports to Eastern gateways, connects with Canada's rail systems, and is the only railroad serving all six major Mexico gateways. Union Pacific provides value to its roughly 10,000 customers by delivering products in a safe, reliable, fuelefficient, and environmentally responsible manner.4
Business Overview
Union Pacific Railroad is a Class I railroad operating in the U.S. Union Pacific has 32,534 route miles, connecting Pacific Coast and Gulf Coast ports with the Midwest and Eastern U.S. gateways and providing several corridors to key Mexican gateways. The company serve the western two-thirds of the country and maintain coordinated schedules with other rail carriers to move freight to and from the Atlantic Coast, the Pacific Coast, the Southeast, the Southwest, Canada, and Mexico. Export and import traffic moves through Gulf Coast, Pacific Coast, and East Coast ports and across the Mexican and Canadian borders. In 2022, the company generated freight revenues totaling $23.2 billion from the following three commodity groups:
Bulk
The Company's Bulk shipments consist of grain and grain products, fertilizer, food and refrigerated, and coal and renewables. In 2022, this group generated 33% of its freight revenues. The company access most major grain markets, connecting the Midwest and Western U.S. producing areas to export terminals in the Pacific Northwest and Gulf Coast ports as well as Mexico. The company also serve significant domestic markets, including grain processors, animal feeders, and ethanol producers in the Midwest and West. Fertilizer movements originate in the Gulf Coast region, Midwest, Western U.S., and Canada (through interline access) for delivery to major agricultural users in those areas as well as abroad. The Railroad’s network supports the transportation of coal shipments to independent and regulated power companies and industrial facilities throughout the U.S. Through interchange gateways and ports, UPRR’s reach extends to Eastern U.S. utilities as well as to Mexico and other international destinations. Coal traffic originating in the Powder River Basin (PRB) area of Wyoming is the largest portion of the Railroad’s coal business. Renewable shipments for customers committed to sustainability consist primarily of biomass exports and wind turbine components.
Industrial
The company's extensive network facilitates the movement of numerous commodities between thousands of origin and destination points throughout North America. The Industrial group consists of several categories, including construction, industrial chemicals, plastics, forest products, specialized products (primarily waste, salt, and roofing), metals and ores, petroleum, liquid petroleum gases (LPG), soda ash, and sand. Transportation of these products accounted for 35% of its freight revenues in 2022. Commercial, residential, and governmental infrastructure investments drive shipments of steel, aggregates, cement, and wood products. Industrial and light manufacturing plants receive steel, nonferrous materials, minerals, and other raw materials.
The industrial chemicals market consists of a vast number of chemical compounds that support the manufacturing of more complex chemicals. Plastics shipments support automotive, housing, and the durable and disposable consumer goods markets. Forest product shipments include lumber and paper commodities. Lumber shipments originate primarily in the Pacific Northwest or Western Canada and move throughout the U.S. for use in new home construction and repairs and remodeling. Paper shipments primarily support packaging needs. Oil and gas drilling generates demand for raw steel, finished pipe, stone, and drilling fluid commodities. The Company’s petroleum and LPG shipments are primarily impacted by refinery utilization rates, regional crude pricing differentials, pipeline capacity, and the use of asphalt for road programs. Soda ash originates in southwestern Wyoming and California, destined for chemical and glass producing markets in North America and abroad.
Premium
In 2022, Premium shipments generated 32% of Union Pacific’s total freight revenues. Premium includes finished automobiles, automotive parts, and merchandise in intermodal containers, both domestic and international. International business consists of import and export traffic moving in 20 or 40-foot shipping containers, that mainly pass through West Coast ports, destined for one of the Company's many inland intermodal terminals. Domestic business includes container and trailer traffic picked up and delivered within North America for intermodal marketing companies (primarily shipper agents and logistics companies) as well as truckload carriers.
Union Pacific is the largest automotive carrier west of the Mississippi River and operate or access 39 vehicle distribution centers. The Railroad’s extensive franchise accesses six vehicle assembly plants and connects to West Coast ports, all six major Mexico gateways, and the Port of Houston to accommodate both import and export shipments. In addition to transporting finished vehicles, the Company provides expedited handling of automotive parts in both boxcars and intermodal containers destined for Mexico, the U.S., and Canada.
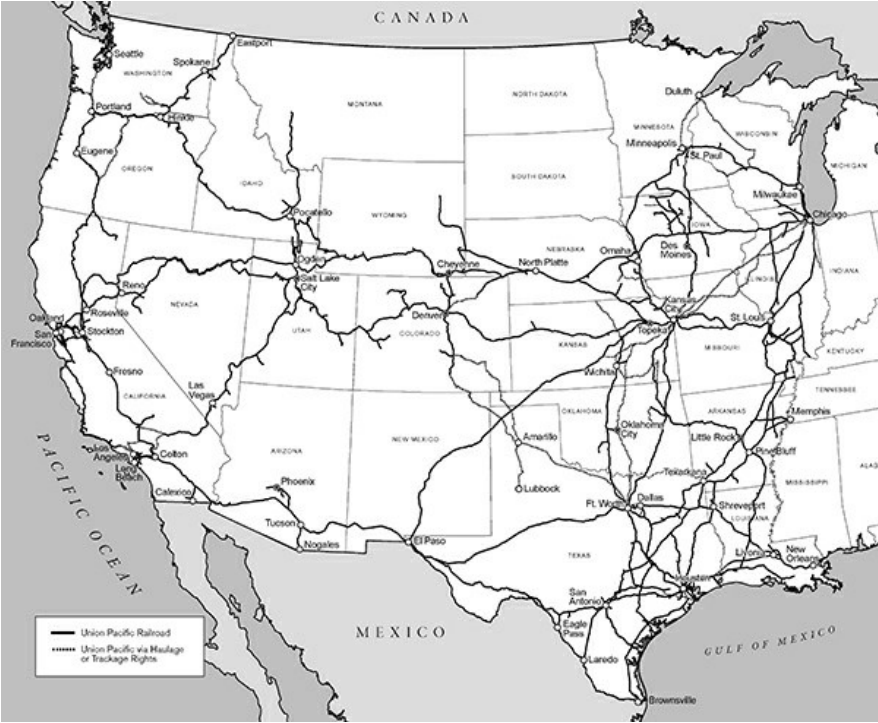
Track
The company's rail network includes 32,534 route miles. The company own 26,121 miles and operate on the remainder pursuant to trackage rights or leases.
| As of December 31, | 2022 | 2021 |
| Route | 32,534 | 32,452 |
| Other main line | 7,113 | 7,093 |
| Passing lines and turnouts | 3,454 | 3,412 |
| Switching and classification yard lines | 8,853 | 8,887 |
| Total miles | 51,954 | 51,844 |
Rail Facilities
In addition to its track structure, the company operate numerous facilities, including terminals for intermodal and other freight; rail yards for building trains (classification yards), switching, storage-in-transit (the temporary storage of customer goods in rail cars prior to shipment), and other activities; offices to administer and manage its operations; dispatching centers to direct traffic on its rail network; crew on duty locations for train crews along its network; and shops and other facilities for fueling, maintenance, and repair of locomotives and repair and maintenance of rail cars and other equipment.
Major Classification Yards
- North Platte, Nebraska
- Englewood (Houston), Texas
- North Little Rock, Arkansas
- Livonia, Louisiana
- West Colton, California
- Fort Worth, Texas
- Houston, Texas
- Roseville, California
Major Intermodal Terminals
- Joliet (Global 4), Illinois
- Global II (Chicago), Illinois
- East Los Angeles, California
- Mesquite, Texas
- Lathrop, California
- LATC (Los Angeles), California
- ICTF (Los Angeles), California
- Marion, Arkansas
Capital Expenditures
The company's rail network requires significant annual capital investments for replacement, improvement, and expansion. These investments enhance safety, support the transportation needs of its customers, improve its operational efficiency, and support emission reduction initiatives outlined in its Climate Action Plan.
2022 Capital Program – During 2022, its capital program totaled approximately $3.4 billion.
2023 Capital Plan – In 2023, the company expect its capital plan to be approximately $3.6 billion, up 6% from 2022.
Company History
Founded July 1, 1862, when President Lincoln signed the Pacific Railway Act, Starting with the construction of the first transcontinental railroad now The Union Pacific Railroad is one of the largest railroads in the United States. It operates over 32,000 miles of track, and it serves more than 230 cities and towns.5
| Year | Milestone |
| 1862 | The Pacific Railway Act is signed by President Abraham Lincoln, which chartered two companies to build a transcontinental railroad: the Union Pacific Railroad and the Central Pacific Railroad. |
| 1863 | Construction begins on the Union Pacific Railroad in Omaha, Nebraska. |
| 1869 | The Union Pacific Railroad reaches Promontory Summit, Utah, where it meets the Central Pacific Railroad, completing the first transcontinental railroad. |
| 1870 | The Union Pacific Railroad is completed, connecting Omaha, Nebraska, to Sacramento, California. |
| 1880s | The Union Pacific Railroad expands its network, reaching into Wyoming, Colorado, Utah, and Nevada. |
| 1900s | The Union Pacific Railroad continues to grow, becoming one of the largest railroads in the United States. |
| 1970s | The Union Pacific Railroad merges with the Southern Pacific Railroad, forming one of the largest railroad companies in the world. |
| 1990s | The Union Pacific Railroad divests itself of its passenger operations, becoming a freight-only railroad. |
| 2000s | The Union Pacific Railroad continues to grow, expanding its network into Mexico and Canada. |
| 2020s | The Union Pacific Railroad is a major player in the global freight transportation market, with a network that spans 23 states and three Canadian provinces. |
References
- ^ https://www.up.com/media/releases/port-houston-intermodal-nr-230530.htm
- ^ https://www.up.com/media/releases/1q23-financial-results-nr-230420.htm
- ^ https://www.up.com/media/releases/4q22-yearend-earnings-nr-230124.htm
- ^ https://fintel.io/doc/sec-union-pacific-corp-100885-10k-2023-february-10-19398-3088
- ^ https://www.up.com/heritage/history/index.htm




